Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM4IF32)
| Drug Name |
Pyrazinamide
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aldinamid; Aldinamide; Braccopiral; Corsazinmid; Dipimide; Eprazin; Farmizina; Isopas; Lynamide; Novamid; Pezetamid; Pharozinamide; Piraldina; Pirazimida; Pirazinamid; Pirazinamida; Pirazinamide; Prazina; Pyrafat; Pyramide; Pyrazide; Pyrazinamdie; Pyrazinamidum; Pyrazineamide; Pyrazinecarboxamide; Rozide; Tebrazid; Tebrazio; Tisamid; Unipyranamide; Zinamide; Zinastat; P ezetamid; Pirazinamide [DCIT]; Pyrazine carboxamide; Pyrazine carboxylamide; Pyrazinecarboxylic acid amide; Pyrazinoic acid am ide; Pyrazinoic acid amide; DRG 0124; MK 56; P 7136; Pyrazinamide BP 2000; T 165; AZT + Pyrazinamide combination; D-50; Pirazinamida [INN-Spanish]; Pms-Pyrazinamide; Pyrazinamide (TN); Pyrazinamidum [INN-Latin]; D-50 (VAN); Pyrazinamide [INN:BAN:JAN]; Pyrazine-2-carboxamide; Pyrazinamide (JP15/USP/INN); Pyrazinoic acid amide, Pezetamid, Pyrafat, Zinamide, Tebrazid, Pyrafat, Pyrazinamide; 2-Carbamylpyrazine; 2-carbamyl pyrazine
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antitubercular Agents
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
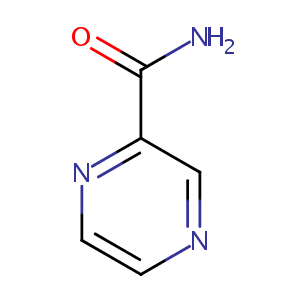 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 123.11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -0.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Pyrazinamide (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Pyrazinamide FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 7287). | ||||
| 3 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 4 | Critical Evaluation of Human Oral Bioavailability for Pharmaceutical Drugs by Using Various Cheminformatics Approaches | ||||
| 5 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | Pyrazinamide inhibits the eukaryotic-like fatty acid synthetase I (FASI) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Med. 2000 Sep;6(9):1043-7. | ||||
| 8 | The metabolism of pyrazoloacridine (NSC 366140) by cytochromes p450 and flavin monooxygenase in human liver microsomes. Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Feb 15;10(4):1471-80. | ||||
| 9 | Specificity and mechanism of Acinetobacter baumanii nicotinamidase: implications for activation of the front-line tuberculosis drug pyrazinamide. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48(48):9176-9. | ||||
| 10 | Pyrazinamide-induced hepatotoxicity is alleviated by 4-PBA via inhibition of the PERK-eIF2-ATF4-CHOP pathway. Toxicology. 2017 Mar 1;378:65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 4. | ||||
| 11 | Clinical and molecular analysis of patients with renal hypouricemia in Japan-influence of URAT1 gene on urinary urate excretion. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004 Jan;15(1):164-73. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000105320.04395.d0. | ||||
| 12 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 13 | Product Information. Aubagio (teriflunomide). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 14 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 15 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 16 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 17 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 18 | Kunimoto D, Warman A, Beckon A, Doering D, Melenka L "Severe hepatotoxicity associated with rifampin-pyrazinamide preventative therapy requiring transplantation in an individual at low risk for hepatotoxicity." Clin Infect Dis 36 (2003): E158-61. [PMID: 12802781] | ||||
| 19 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 20 | Elsharkawy AM, Schwab U, McCarron B, et al. "Efavirenz induced acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation in a slow drug metaboliser." J Clin Virol 58 (2013): 331-3. [PMID: 23763943] | ||||
| 21 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 22 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 24 | Blakely KM, Drucker AM, Rosen CF "Drug-induced photosensitivity-an update: Culprit drugs, prevention and management." Drug Saf 42 (2019): 827-47. [PMID: 30888626] | ||||
| 25 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Clolar (clofarabine). sanofi-aventis, Bridgewater, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. ReVia (naltrexone). DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE. | ||||
